
You also can write non-homogeneous differential equations in this format: y” + p(x)y’ + q(x)y = g(x). The interesting part of solving non homogeneous equations is having to guess your way through some parts of the solution process. Non-homogeneous differential equations are the same as homogeneous differential equations, However they can have terms involving only x, (and constants) on the right side. I would recommend you watch them if you are still confused about Repeated Roots of Second order linear homogeneous equation. The following three videos are form Khan Academy.
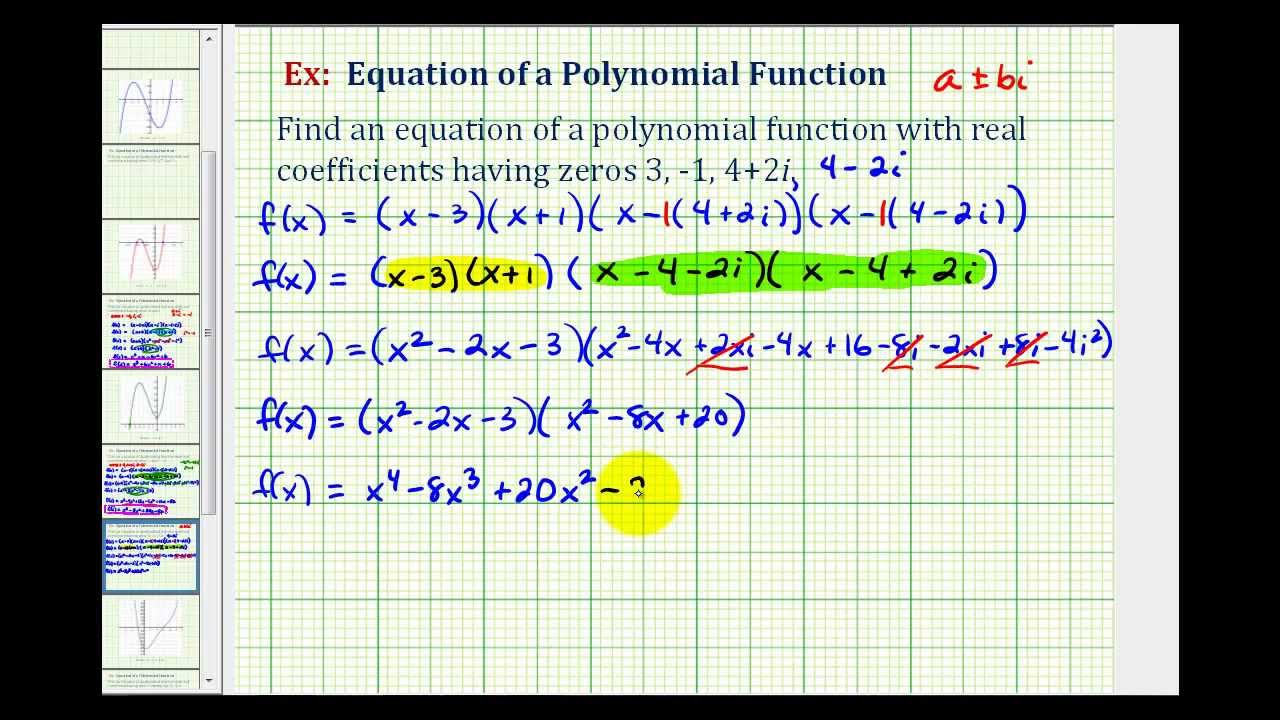
Step 4: Plug r 1 and r 2 into the general solution for the repeated roots Step 3: Use y = e rt as a solution for r 1 and r 2 Step 2: Factor the characteristic equation Step 1: Turn the differential equation into a characteristic equation The general solution for the repeated root will then be in the following form: In order to avoid this a “t” needs to be place in the general solution. The next step would be to plug r 1 and r 2 into the general equation:Īnother important thing to realize and remember is that when solving a homogeneous equation for a repeated root the solution will end up cancelling out. Once you get repeated roots, or r 1 and r 2 from the characteristic equation then y = e rt is considered a solution of the differential equation. The quadratic equation will the look like the following: In the cases where there is no a variable limit the a variable from the quadratic equation. There will problems where the variable a is not needed in the quadratic formula because there will be no a in the differential equation. It is important to remember when to the particular equation above. Second to find the roots, or r 1 and r 2 you can either factor or use the quadratic formula:
The characteristic equation is written in the following form: The first step is to use the equation above to turn the differential equation into a characteristic equation.
#CHARACTERISTIC EQUATION CALCULATOR HOW TO#
This guide will be discussing how to solve homogeneous linear second order differential equation with constant coefficient, which is written in the following form: Second order linear equations become homogeneous when the linear function of y and y’ (which can be written in the form y” + p(t)y’ + q(t)y = g(t)) is equal to zero.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
